Supply chains and blockchain: transforming the fulfillment industry

Imagine a world where your order arrives not only on time but with a clear, verifiable story behind it. You know exactly where each product came from, how it was made, and what steps it took to get to your doorstep. In a way, this is already becoming a reality thanks to the powerful technology behind blockchain. But the journey to this kind of transparency hasn’t been easy.
For years, supply chains operated with a mix of good intentions and best practices – lean models and just-in-time strategies. But then came the disruptions: geopolitical tensions, cyberattacks, inflation, climate change, and global pandemics. Suddenly, the flawless supply chains we once took for granted seemed fragile, vulnerable to any small disruption. Retailers couldn’t restock fast enough, and consumers started feeling the consequences, from delayed deliveries to empty shelves. As businesses reeled from these shocks, they realized that to survive in a world of uncertainty, their supply chains had to evolve. And that’s where blockchain comes in.
Blockchain promises to be the cornerstone of the new generation of supply chains – ones that are not only resilient but transparent, trustworthy, and efficient. It is more than just a buzzword. It’s a transformative tool that is already reshaping how businesses operate and how consumers experience the fulfillment process. But let’s dive into the story of how blockchain is changing the game.
Advantages of blockchain technology in logistics.
The role of blockchain in supply chain management
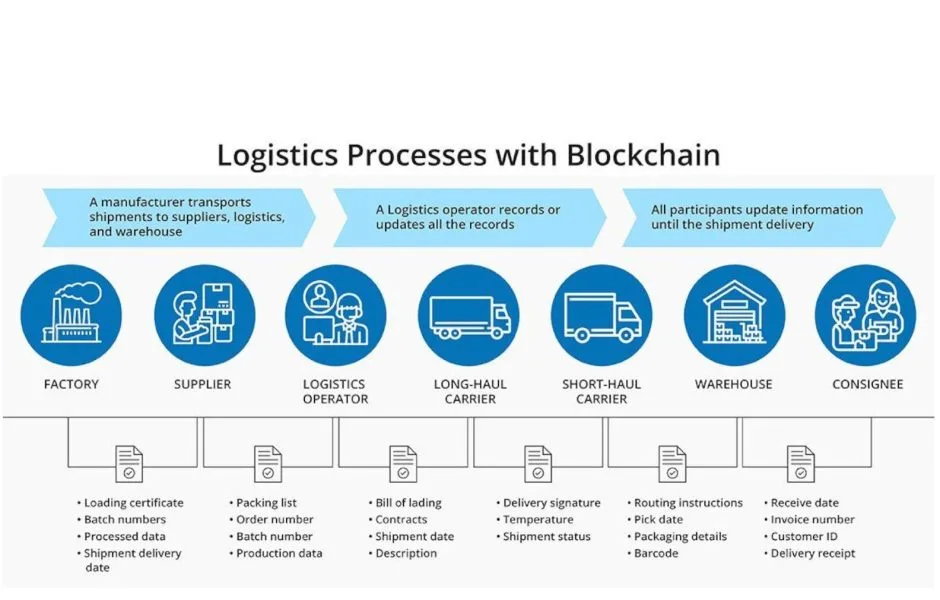
At its core, blockchain is a technology that creates a shared, immutable ledger of transactions. Think of it like a digital diary that records every event in a product’s journey—from raw materials to the final delivery. Each step is documented and verified in a way that no one can alter, ensuring that all parties in the supply chain have access to the same accurate information. This transparency doesn’t just improve trust; it fosters it.
Now, imagine a scenario where a manufacturer and a supplier, even if miles apart, can check on the exact status of a product’s materials in real-time. Blockchain enables this, making it easier to track materials, ensure compliance with environmental standards (like Scope 3 emissions), and quickly identify potential risks before they escalate.
In a world where information often distorts, blockchain ensures nothing gets lost in translation. It allows businesses to see and verify data that is shared across different stakeholders. Whether it’s a supplier in Asia, a logistics company in Europe, or a retailer in North America. It’s like giving every player in the supply chain a direct window into the truth. The result? More secure, efficient, and predictable operations that ultimately benefit both businesses and consumers.

The impact on fulfillment: from chaos to clarity
In the fast-paced world of fulfillment, every second counts. Blockchain steps in to make those seconds matter. Let’s take a look at how this transformative technology improves different aspects of the fulfillment process.
1. Real-time inventory tracking: the end of stockouts and discrepancies
Picture a warehouse where inventory tracking has always been a challenge. Stock counts are often inaccurate, orders get delayed because products aren’t where they should be, and communication between warehouses is fragmented. Blockchain provides a solution by offering real-time updates on inventory levels, ensuring that each item is accounted for, no matter where it is in the supply chain. Blockchain eliminates inventory discrepancies and stockouts. Everything is visible and up-to-date, meaning businesses can respond faster and reduce costly mistakes.
2. Efficient order fulfillment: speed, accuracy, and automation
Now think about order fulfillment, where speed and accuracy make all the difference. A customer places an order, and within minutes, a smart contract triggers. This digital contract automatically verifies the order, processes payment, and even ensures the correct routing for delivery, based on real-time data like weather conditions or traffic patterns. It’s all automated. No human error. Just smooth, fast processing that reduces delays and improves delivery times. Blockchain doesn’t just automate; it optimizes.
3. Enhanced visibility and trust: building relationships through transparency
In the world of fulfillment, transparency is key. Blockchain creates a level playing field for all participants, offering real-time traceability that enhances accountability. Consumers can track their products from manufacturer to doorstep, ensuring authenticity at every step. It’s more than just verifying a product’s origin—it’s about fostering trust. When a company uses blockchain, it’s telling customers, “You can trust us because you can see exactly where your product has been and how it got here.”
4. Customer experience: more than just delivery
The fulfillment process is ultimately about the customer. And blockchain improves their experience at every stage. Imagine being able to track your order in real-time and knowing exactly when it will arrive – without surprises. Through blockchain, customers get instant updates on their orders, leading to fewer frustrations and more satisfaction. And with automated delivery routing, blockchain can even help deliver your product faster, increasing customer loyalty and trust.
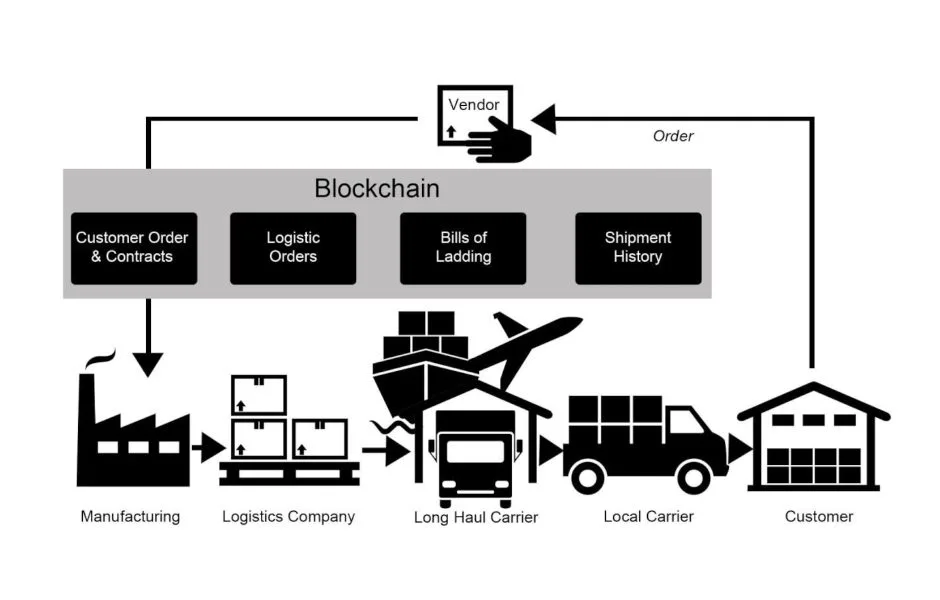
Smart contracts: the unsung hero of fulfillment
What makes blockchain even more powerful are smart contracts – programs that automatically execute agreements based on predefined conditions. These contracts are the silent workers behind the scenes. They ensure that once an order is placed, everything flows smoothly: from verifying payment to triggering shipments, to confirming deliveries.
Imagine a scenario where a supplier delivers goods to a warehouse. Once the warehouse receives and scans the goods, the smart contract automatically releases payment. No delays. No paperwork. No misunderstandings. It’s a perfect example of how blockchain, combined with smart contracts, removes friction and streamlines processes—saving both time and money.
Application of smart contracts in logistics.
Data security and privacy: the backbone of trust
In a world where data breaches are becoming increasingly common, blockchain offers a rare layer of security. With its decentralized architecture and encryption techniques, blockchain makes it nearly impossible for hackers to manipulate the system. Whether it’s customer data, payment details, or inventory levels, blockchain keeps everything safe and sound.
Furthermore, because every transaction records on an immutable ledger, businesses can quickly spot discrepancies or suspicious activities. Blockchain provides a secure and transparent environment, protecting data privacy and ensuring information flows only to those who need it.
Cost reduction and efficiency: less waste, more profit
Now, let’s talk about the bottom line: cost. Blockchain significantly reduces operational costs by automating manual processes. Inventory management, order fulfillment, and payments are all streamlined, cutting down on labor costs and administrative overhead. By reducing stockouts, eliminating fraud, and minimizing delays, blockchain ensures that businesses operate more efficiently.
Additionally, blockchain helps companies cut costs in ways that go beyond just improving operational efficiencies. For instance, by verifying the authenticity of products and preventing counterfeiting, businesses reduce the risk of fraudulent claims and unnecessary returns. With better visibility and smarter decision-making, companies can improve cash flow and boost their bottom line.
Returns management: simplifying a complex process
One area where blockchain truly shines is returns management, a crucial yet often overlooked aspect of fulfillment. Returns can be a costly and confusing process for both businesses and customers. But with blockchain, every return is tracked from start to finish on a transparent and immutable ledger. This means no more disputes over whether a product is eligible for return, as all the transaction history is available for review.
Furthermore, smart contracts automate the returns process by triggering refunds and exchanges as soon as conditions are met. This reduces delays, cuts administrative costs, and improves the customer experience—transforming a traditionally complicated process into something straightforward and efficient.

Potential challenges: the road ahead
Despite its vast potential, implementing blockchain is not without its challenges. Initial costs can be high, particularly for small to medium-sized businesses. Setting up the infrastructure, training employees, and integrating blockchain with existing systems require both time and investment. Additionally, as blockchain is still evolving, compatibility with other technologies could pose hurdles.
Moreover, blockchain relies on high-quality data from all participants in the supply chain. If the data isn’t accurate or consistent, it could undermine the entire system’s effectiveness. There’s also the question of privacy, as the transparency that blockchain provides may raise concerns about data sharing among stakeholders.
Conclusion: a new era for fulfillment
The transformation is already happening. Blockchain is not just a trend; it changes the way businesses manage supply chains and handle fulfillment. By improving visibility, enhancing trust, and streamlining operations, blockchain is not only making fulfillment more efficient but also more secure, transparent, and customer-centric. The future of fulfillment is blockchain-powered. Businesses that embrace this technology will position themselves to thrive in an increasingly complex and fast-paced world.
More interesting articles on blockchain technology in supply chains:



