What Is eCommerce Fulfillment?
Let’s delve into the world of eCommerce fulfillment to explore its key elements, strategies, challenges, and best practices.
The internet revolutionized the way we shop. And with ever-increasing demand for online shopping, retailers and brands need to find the right eCommerce fulfillment solution to win sales and deliver to customers. From order processing to inventory management, warehousing, and shipping and returns management, every step of the eCommerce fulfillment process plays a role in delivering a seamless customer experience.
But what is eCommerce fulfillment? Let’s explore the different models, challenges, and best practices required to deliver success from click to delivery.

In this Article
What is the Definition of eCommerce Fulfillment?
Who Needs eCommerce Fulfillment?
How Does eCommerce Fulfillment Work?
Value-Added Services
What Are the Different Types of eCommerce Fulfillment?
What are Common eCommerce Fulfillment Challenges?
How do Retailers Choose the Right Fulfillment Model?
How Do You Choose a Third-Party eCommerce Fulfillment Partner?
What are the Benefits of Working with a Third-Party eCommerce Fulfillment Partner?
What are eCommerce Fulfillment Best Practices?
eCommerce Fulfillment FAQs
What is the Definition of eCommerce Fulfillment?
eCommerce fulfillment is the process of getting an online order delivered to a customer. It includes all the logistics functions necessary to store goods, manage inventories, process and pack orders, deliver purchases, and process returns.
Who Needs eCommerce Fulfillment?
Any retailer or brand that sells products online needs an eCommerce fulfillment strategy to be successful. Optimized eCommerce fulfillment ensures customers receive their orders accurately and promptly—all while maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
How Does eCommerce Fulfillment Work?
The eCommerce fulfillment process consists of different sub-processes, all designed to support the successful storage, processing and packing, and delivery of online orders.
Warehousing
Warehousing involves the organization and storage of goods. Where warehouses are located and how they are structured, organized, staffed, and operated directly affects the rest of the eCommerce fulfillment process.
Order Processing
Order processing is the series of tasks involved in receiving, reviewing, and preparing customer orders for shipment. It encompasses all the steps from the moment a customer places an order online with your eCommerce store to the point where the order is ready for shipping.
The order processing workflow varies depending on the specific business and its systems, but it typically includes the following steps:
- Order receipt: When a customer places an order with an online business, the order details are received electronically, generating a work order. The order information is then forwarded to the eCommerce fulfillment center for processing.
- Order verification: The fulfillment team reviews the order details to ensure that all necessary information is complete and accurate. This includes verifying the customer’s contact details, shipping address, product selection, quantities, and any special instructions or requests.
- Inventory check: The inventory management system is checked to determine the availability of the ordered items, confirming whether the products are in stock or if any items are backordered or out of stock.
- Payment verification: The payment associated with the order is verified to ensure it has been successfully processed and received. The verification process prevents fraud and ensures the order can proceed to the next stage.
- Order fulfillment: Once the order has passed the verification process and the items are confirmed to be in stock, the fulfillment team retrieves the products from the warehouse shelves and processes them for delivery.
Inventory Management and Forecasting
Inventory management and forecasting involve the processes and techniques needed to effectively track, control, and predict inventory levels to meet customer demand. It helps businesses ensure they have the right amount of inventory at the right time and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
- Stock monitoring: Businesses regularly monitor inventory levels to track the quantity of each product available. This is typically done using an inventory management system that keeps a real-time record of stock levels and updates it with each sale or restocking activity.
- Inventory forecasting: Logistics leaders analyze historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant factors to estimate the demand for their products. They can then determine optimal inventory levels and replenishment schedules. Accurate inventory forecasting means businesses can optimize inventory levels across multiple nodes, minimize holding costs, avoid stockouts, and efficiently meet customer demand. It helps strike a balance between having enough inventory to fulfill orders promptly and avoiding excess stock that ties up capital.
- SKU management: Each unique product variant or stock-keeping unit (SKU) is tracked individually. This allows businesses to monitor the performance of specific products, analyze sales patterns, and make informed decisions about restocking, promotions, or discontinuing certain SKUs.
Packaging and Shipping
Before an item is packed and shipped, it will go through quality control to ensure the product meets the business’s standards. Packaging and shipping consist of a process called pick and pack, where ordered items are retrieved from the warehouse shelves and securely packed for shipment. Depending on the business, it may also consist of a process called kitting, as well as value-added services that include personalization.
- Kitting and assembly: During kitting and assembly, multiple individual items are assembled into a single package or kit. It involves combining different products or parts that are often sold together as a set or used together in a specific application.
- Picking and packing: In contrast to kitting, picking and packing focus on fulfilling individual customer orders by selecting the requested items and packaging them for shipment. These processes are typically performed for each order received, whereas kitting is more commonly done in advance to create an inventory of pre-assembled kits.
Value-Added Services
Value-added services may also be involved in the packaging and shipping process. Value-added services refer to additional services or enhancements beyond the basic picking, packing, and shipping of products. These services provide added value to customers, improve the overall shopping experience, and differentiate an eCommerce business from its competitors. Common examples of value-added services in eCommerce fulfillment include:
- Gift wrapping: Offering gift wrapping services allows customers to have their orders wrapped in special packaging, making them suitable for gifting. This service can include personalized messages, gift cards, or decorative elements.
- Customization and personalization: Providing options for customers to customize or personalize products enhances their experience. This could involve engraving, monogramming, or adding custom designs to items, allowing customers to create unique and personalized products.
Returns Management
The eCommerce fulfillment process also includes managing returns and providing customer support. This may involve processing returns, issuing refunds or exchanges, and addressing customer inquiries or complaints.
Returns management includes managing product returns initiated by customers for various reasons, such as product defects, wrong sizing, change of mind, or damaged items. This involves establishing clear return policies, providing return labels or instructions, inspecting returned products, and determining appropriate actions based on the condition of the items.
Functions include:
- Return authorization and tracking: A return authorization process helps track and manage returned products. This involves issuing return authorization numbers or labels to customers, which allows the eCommerce business to identify and track the returned items throughout the reverse logistics process.
- Inspection and assessment: Upon receiving returned products, retailers perform a thorough inspection to assess their condition. This includes checking for any damage, missing parts, or signs of wear that may affect the product’s resale value or eligibility for a refund or exchange.
- Refunds and exchanges: Returns management involves processing refunds or exchanges for returned products based on established return policies. This may include issuing refunds to customers’ original payment methods, providing store credits, or facilitating exchanges for different products or sizes.
- Inventory management: In some cases, products can be returned to the shelves after they have been returned, which means managing inventory levels by updating inventory records, segregating returned items, and accounting for their availability for secondary markets or further processing.

What Are the Different Types of eCommerce Fulfillment?
Each retailer and brand can assess and implement eCommerce fulfillment strategies differently:
B2C eCommerce Fulfillment
B2C (Business-to-Consumer) fulfillment focuses on fulfilling orders placed by individual consumers. That means managing a high volume of smaller orders, often with short delivery windows and high customer expectations.
B2C fulfillment processes typically prioritize speed and accuracy, with services such as same-day or next-day delivery, order tracking, and easy returns processing. B2C fulfillment providers often utilize advanced technology and logistics solutions to optimize the customer experience and streamline operations.
B2B eCommerce Fulfillment
B2B (Business-to-Business) fulfillment involves fulfilling orders placed by businesses for goods or services. This process often requires specialized solutions tailored to the unique needs of B2B transactions. It includes managing bulk orders, negotiating pricing and terms, handling complex shipping requirements, and providing customized invoicing and payment options.
B2B fulfillment providers typically offer services such as advanced order management systems, scalable warehouse operations, flexible inventory management, and enhanced account support tailored to the needs of business clients.
Enterprise eCommerce Fulfillment
Enterprise fulfillment involves catering to the needs of large-scale businesses with extensive product lines and complex supply chains. It requires robust, highly scalable logistics infrastructure capable of handling high volumes of orders efficiently while maintaining accuracy and reliability.
Mid-Market eCommerce Fulfillment
Mid-market fulfillment serves businesses that fall between small-scale operations and large enterprises. It involves balancing cost effectiveness with the ability to scale as the business grows. This segment often requires flexible solutions that can adapt to changing demand patterns and market dynamics while still providing quality service to customers.
International eCommerce Fulfillment
At its core, international fulfillment encompasses the processes of receiving, processing, and delivering orders to global customers in different countries. This includes managing inventory across multiple locations, coordinating shipping and customs clearance, and ensuring timely delivery to customers worldwide.
What are Common eCommerce Fulfillment Challenges?
Organizations face a variety of challenges when executing eCommerce fulfillment processes. These include inventory inaccuracy, order errors, shipping delays, returns issues, fragmented data, and even international shipping challenges.
Inventory Inaccuracy
It’s challenging to maintain accurate inventory levels across multiple sales channels. It’s crucial to avoid stockouts or overstock situations that can lead to lost sales or increased holding costs. Managing inventory across different warehouses or fulfillment centers adds complexity to the process.
Order Errors and Shipping Delays
Customers expect fast delivery times, and they shop at businesses that offer faster shipping. Unfortunately, fast shipping requires efficient order processing, inventory management, and warehouse operations some small businesses may not have.
Errors in picking, packing, or shipping can result in incorrect products, delayed deliveries, and increased returns. Managing high order volumes during peak seasons puts pressure on fulfillment operations.
Returns Issues and Returns Fraud
Managing product returns, exchanges, and refunds can be complex and time-consuming. It requires effective systems and processes to process returns efficiently, inspect returned items, and manage reverse logistics. And it’s crucial to balance customer satisfaction with cost-effective return policies.
Fragmented Data and Poor Reporting
Don’t let fragmented, inaccurate, or inconsistent data sources affect your bottom line and ability to retain customers. Many eCommerce companies use a mix of legacy and cloud systems that are difficult to integrate and maintain, making it difficult to see real-time data across the supply chain.
International Shipping Challenges
Expanding into international markets introduces new challenges, such as customs regulations, international shipping costs, and cross-border logistics. Smooth international fulfillment requires understanding and complying with different countries’ legal requirements and customs procedures.
Shipping products internationally means working with multiple logistics providers, shipping carriers, and customs brokers. Coordinating the movement of goods across borders, managing different shipping options, and ensuring timely delivery can be challenging. Distance, transit times, customs clearance, and potential disruptions can impact the shipping experience.
Good cross-border eCommerce also requires processing payments in different currencies and converting prices accurately. Managing currency fluctuations, handling exchange rates, and offering secure and convenient payment options for international customers can be complex.
Lastly, handling returns and customer service inquiries for cross-border orders adds complexity. Managing international returns processes, addressing language barriers, and ensuring smooth communication with customers across different time zones can be demanding.

How do Retailers Choose the Right Fulfillment Model?
In-House Fulfillment
With an in-house fulfillment model, also known as merchant fulfillment, the eCommerce retailer handles all aspects of fulfillment internally, including warehousing, inventory management, order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. The business maintains its own fulfillment centers or warehouses to store inventory, and the entire fulfillment process is managed by the company’s own staff.
In-house fulfillment provides businesses with greater control over the fulfillment process and allows for more customization and flexibility. But it requires significant infrastructure, resources, and expertise to effectively manage fulfillment operations.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where the eCommerce business doesn’t hold inventory or handle product fulfillment directly. Instead, when a customer places an order, the business forwards the order details to a supplier or manufacturer, who then ships the products directly to the customer.
The eCommerce business acts as an intermediary, taking orders and payments from customers and passing on the order information to the supplier for fulfillment. Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management and upfront investment in stock. Merchants instead focus on marketing, customer acquisition, and building their online presence.
There are potential drawbacks. Dropshipping may result in less control over product availability, shipping times, and customer experience, as these aspects are managed by the supplier.
Amazon FBA
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a fulfillment service that grants retailers access to Amazon’s logistics network. FBA ships orders from Amazon Marketplace and other eCommerce platforms. It also gives retailers Amazon Prime shipping. There are potential challenges, however. FBA warehouse space can be limited, especially during peak demand periods. There are also minimum sales requirements that smaller brands may not be able to meet. FBA also doesn’t ship bulky products.
Outsourced Fulfillment / Third-Party Logistics
Many growing eCommerce retailers outsource fulfillment to third-party logistics partners (3PLs). 3PLs are specialized fulfillment companies that manage warehousing, inventory storage, order processing, kitting or gift wrapping, shipping, and returns on behalf of merchants.
The 3PL provider typically has expertise in fulfillment operations, established warehousing infrastructure, and advanced systems to handle the entire process efficiently. This model allows businesses to focus on core activities such as marketing and product development, while relying on the expertise of the 3PL provider for an efficient order fulfillment process. It offers scalability, reduces operational costs, and provides access to specialized fulfillment services.

How Do You Choose a Third-Party eCommerce Fulfillment Partner?
Retailers and brands should consider a variety of factors when evaluating third-party eCommerce fulfillment partners (also known as a 3PL). Here are some important things to look for:
- 3PL eCommerce Expertise and Industry Experience: Assess the 3PL provider’s overall eCommerce expertise and experience in your specific industry or niche. How many years have they been in operation? What are their core competencies? Look for their track record of successfully serving businesses similar to yours. An experienced 3PL will understand the unique logistics requirements and challenges of your industry—especially when it comes to online fulfillment.
- 3PL Range of Services: Evaluate the range of services offered by the 3PL. Consider whether they provide the specific logistics functions you require, like warehousing, transportation, inventory management, order processing and fulfillment, returns, and value-added services. Choose a provider that offers what you need now—and what you might need as you scale.
- 3PL Scalability and Flexibility: Assess the 3PL’s ability to scale operations and adapt to changing business requirements. Do they have the resources, infrastructure, and network necessary to handle demand fluctuations, seasonal peaks, and future growth? A flexible 3PL will be able to adjust their services to accommodate your evolving needs.
- 3PL Technology and Systems: Evaluate the technology and automation systems employed by the 3PL. Look for advanced logistics software, warehouse management systems, order management systems, and real-time tracking capabilities.
- 3PL Warehouse Network and Geographic Coverage: Consider the geographic reach and network while assessing the 3PL warehouse locations, transportation routes, and distribution capabilities. Choosing a 3PL with a network that aligns with your customer base will mean efficient and timely deliveries to your target markets. This is important, since fast, efficient delivery is something that is increasingly important to win online shoppers.
- 3PL Customer References and Reputation: Seek customer references from comparable online retailers or testimonials from businesses that have worked with the 3PL provider. Research their reputation in the industry and look for feedback on their reliability, responsiveness, and overall performance.
- 3PL Cost Structure and Transparency: Assess the cost structure and pricing model of the 3PL. Understand how their fees are calculated, including any additional charges for value-added services or peak season surcharges. Transparency in pricing and billing practices is essential for budgeting and avoiding unexpected costs.
- 3PL Customer Support, Communication, and Collaboration: Consider the 3PL’s communication channels and accessibility. Look for a provider that maintains open lines of communication, provides regular updates on order status, and offers dedicated account management or customer support. Effective collaboration and clear communication are crucial for a successful partnership.
- 3PL Compliance and Security: Verify that the 3PL provider adheres to necessary regulatory compliance, such as customs regulations, industry standards, and security protocols. Assess their certifications, licenses, and security measures for the safety and integrity of your products.
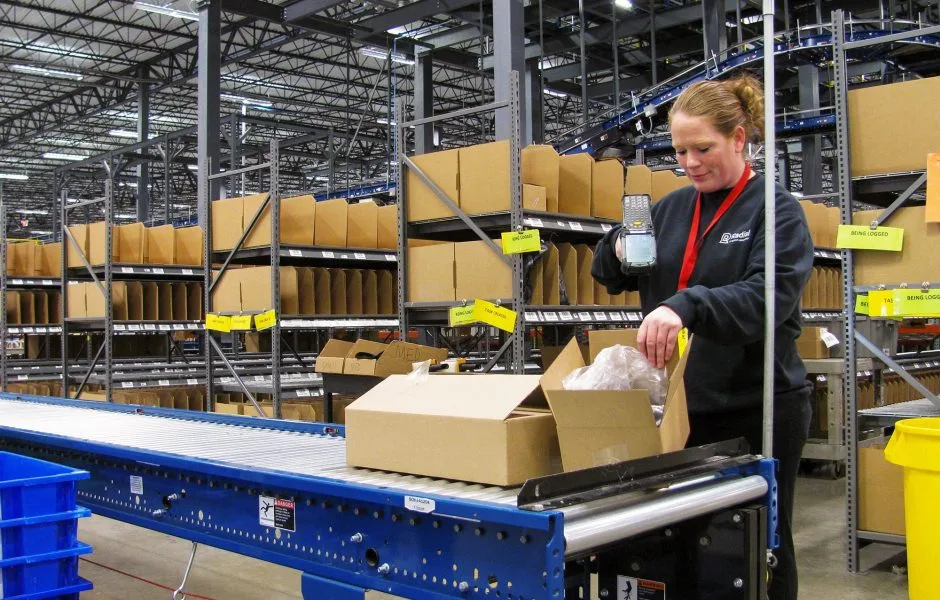

What are the Benefits of Working with a Third-Party eCommerce Fulfillment Partner?
Working with a third-party logistics provider offers retailers and brands a variety of benefits—from outsourced operations to enhanced flexibility and cost savings.
Streamlined Operations and Cost Savings
One advantage of partnering with a 3PL: Retailers can streamline their operations and create cost savings. 3PLs offer dedicated warehouse infrastructure, resources, and operational experience to reduce overall costs and manage supply chains.
By outsourcing functions like warehousing, transportation, inventory management, order fulfillment, shipping, and returns to a specialized provider, businesses can tap into economies of scale, benefit from established networks, and access cutting-edge technology and infrastructure without the need for substantial upfront investments. Companies can then focus on their own core competencies, leaving the complexities of logistics management to the experts.
Flexibility and Scalability
3PLs offer flexibility and scalability to growing retailers and brands. As these companies evolve, their logistics needs will change. 3PLs handle fluctuations in demand, seasonal spikes, and sudden supply chain shifts. Plus, with their pre-existing networks and resources, they can rapidly adapt to change and scale operations up or down as needed. That creates a competitive advantage. Now retailers can respond quickly to market dynamics and customer demands—all while maintaining high levels of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility and Analytics
It’s vital that modern brands have access to the data and analytics necessary to manage their supply chains, and 3PLs can provide the technology, advanced tracking, and robust reporting required for the job. This transparency leads to better decision-making, identification of bottlenecks or inefficiencies, and opportunities for continuous improvement.
Risk Mitigation and Expertise
Supply chains are complex, and uncertainty is at an all-time high. 3PLs mitigate risks and ensure compliance with regulations and industry best practices. They can bring extensive industry knowledge, regulatory expertise, and risk management protocols to brands as well. By leveraging their expertise, businesses can minimize risks, improve compliance, and build resilience within their supply chains.

What are eCommerce Fulfillment Best Practices?
Provide Transparent and Accurate Order Tracking
Customers value visibility and transparency. By providing real-time order tracking information, businesses can keep customers informed about the status and location of their packages. This can be achieved through email notifications, SMS alerts, or an online tracking portal.
Offer a Portfolio of Shipping Options
Every customer has unique preferences and requirements when it comes to shipping. Offer a variety of shipping options so customers can choose the one that best suits their needs—whether it’s based on speed, cost, or convenience. This could include options like standard, express, overnight, or even same-day delivery in certain areas. Businesses can collaborate with multiple shipping carriers and logistics providers to offer a range of shipping options. By catering to different customer preferences, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, increase conversion rates, and stay competitive in the market.
Leverage High Quality Packaging
Packaging is more than just a means to protect products during transit; it also reflects the brand’s image and can create a positive unboxing experience for customers. Investing in high-quality packaging materials and designing branded packaging can elevate the overall customer experience. Consider using sturdy boxes, cushioning materials, and eco-friendly packaging options where possible.
Well-designed packaging that aligns with your brand’s aesthetic can leave a lasting impression on customers and potentially encourage them to share their experiences on social media or recommend your brand to others. It’s important to strike a balance between protective packaging and eco-conscious practices to minimize waste while ensuring products arrive intact.
Optimize Returns Management
Returns are an inevitable part of eCommerce, and how businesses handle them significantly affects customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. To implement a strong returns management process, start by establishing clear and customer-friendly return policies, making it easy for customers to initiate returns and exchanges.
Streamline the returns process by providing pre-paid return labels or arranging for pick-up services where possible. Efficiently inspect returned products to determine their condition and eligibility for resale. Integrate and automate returns management into your fulfillment system to help streamline the process, ensure prompt refunds or replacements, and provide valuable insights into return reasons and trends. Prioritize customer support and communication throughout the returns process to demonstrate your commitment to customer satisfaction.
eCommerce Fulfillment FAQs
What is eCommerce Fulfillment?
eCommerce fulfillment is the process of getting an online order delivered to a customer. It includes all the logistics functions necessary to store goods, manage inventories, process and pack orders, deliver purchases, and process returns.
What is the Difference Between Fulfillment and Shipping?
Fulfillment includes order processing, packaging, and delivery to customers. It involves order management, inventory management, warehousing, and shipping. Shipping, on the other hand, refers just to transporting packages from the fulfillment center to the customer’s location.
What is an eCommerce Fulfillment Partner?
An eCommerce fulfillment partner, also known as a third-party logistics provider (3PL), is an outsourced supply chain partner that helps organizations manage and improve their eCommerce fulfillment operations. Sometimes 3PL companies are described by different names, like fulfillment and distribution companies, fulfillment warehouses, or fulfillment centers.
What are the Different Models of eCommerce Fulfillment?
There are a variety of different eCommerce fulfillment models:
- In-House Fulfillment: With an in-house fulfillment model, also known as merchant fulfillment, the eCommerce retailer handles all aspects of fulfillment internally, including warehousing, inventory management, order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. The business maintains its own fulfillment centers or warehouses to store inventory, and the entire fulfillment process is managed by the company’s own staff. In-house fulfillment provides businesses with greater control over the fulfillment process and allows for more customization and flexibility. But it requires significant infrastructure, resources, and expertise to effectively manage fulfillment operations.
- Dropshipping: Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where the eCommerce business doesn’t hold inventory or handle product fulfillment directly. Instead, when a customer places an order, the business forwards the order details to a supplier or manufacturer, who then ships the products directly to the customer. The eCommerce business acts as an intermediary, taking orders and payments from customers and passing on the order information to the supplier for fulfillment. Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management and upfront investment in stock. Merchants instead focus on marketing, customer acquisition, and building their online presence. There are potential drawbacks. Dropshipping may result in less control over product availability, shipping times, and customer experience, as these aspects are managed by the supplier.
- Amazon FBA: Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a fulfillment service that grants retailers access to Amazon’s logistics network. FBA ships orders from Amazon Marketplace and other eCommerce platforms. It also gives retailers Amazon Prime shipping. There are potential challenges, however. FBA warehouse space can be limited, especially during peak demand periods. There are also minimum sales requirements that smaller brands may not be able to meet. FBA also doesn’t ship bulky products.
- Third-Party Logistics: Many growing eCommerce retailers outsource fulfillment to third-party logistics partners (3PLs). 3PLs are specialized fulfillment companies that manage warehousing, inventory storage, order processing, kitting or gift wrapping, shipping, and returns on behalf of merchants. The 3PL provider typically has expertise in fulfillment operations, established warehousing infrastructure, and advanced systems to handle the entire process efficiently. This model allows businesses to focus on core activities such as marketing and product development, while relying on the expertise of the 3PL provider for an efficient order fulfillment process. It offers scalability, reduces operational costs, and provides access to specialized fulfillment services.
How Much Does eCommerce Fulfillment Cost?
Shipping rates, storage fees, warehouse management costs, and more can impact your bottom line. The cost of eCommerce fulfillment varies based on factors such as order volume, product size, storage requirements, and value-added services.
In-house fulfillment involves warehousing, labor, technology, and shipping costs. Conversely, outsourcing to a 3PL provider typically involves fees based on services provided, such as storage, picking, packing, and shipping. Plan to request quotes from multiple providers and compare costs to make an informed decision.
Interested in Radial’s fulfillment services?
